Molecular Orbital Theory Worksheet
Back to the other Bond Theory Chemistry Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Solutions Manual
- Orbitals are ________ functions. One property of waves is that they can ___________ or _________ interfere with each other.
- What is constructive interference?
- What is destructive interference?
- How does this relate to our understanding of orbital interactions?
- What is Molecular Orbital Theory?
- Facts about molecular orbitals?
- Why do bonds occur?
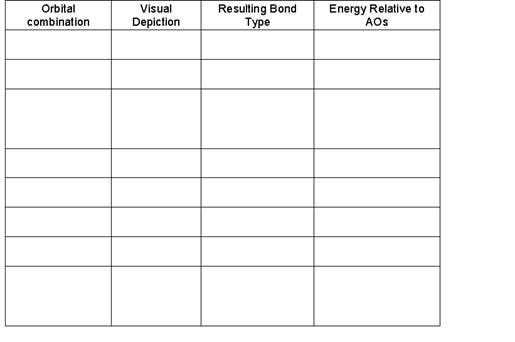
- Fill in the following chart
- What is a Molecular Orbital Diagram?
- Draw the Molecular Orbital Diagram
- H2
- H2+
- H2-
- What is bond order?
- Some facts about bond order:
- What do the bond orders for #12 tell us about relative stabilities of H2 , H2+ ,H2-
- _______________ substances have ____________ electrons and are therefore attracted toward a magnetic field.
_______________ substances have ____________ electrons and are therefore repelled by a magnetic field
- What is the order of molecular orbitals for B2, C2 and N2?
- What is the order of molecular orbitals for O2 and F2?
- Draw the Molecular orbital diagrams for N2 and O2.
- Why do B2, C2 and N2 have a different MO order compared to O2 and F2?
- Given:
N22-, O22-, F22-
- Write out the MO electron configuration for each.
- Which is predicted to be the most stable diatomic species?
- Indicate whether each is paramagnetic or diamagnetic.
- Use the MO model to predict the bond order and magnetism for Ne2 and P2.
- Complete the MO diagram for NO.
- How do we reconcile these two theories (i.e. LE and MO models)?
